What is cybersecurity? Different Types of Cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is a set of standards and practices for organizations to use to prevent an organization’s applications, protocols, data, programs, ports, networks, and systems from cyberattacks and unauthorized access. As hackers deploy new tricks and social engineering to extort money from users and organizations, interfere with business operations, and steal or destroy sensitive data, cybersecurity threats are becoming more sophisticated by the day.
To be protected against these unwanted activities, organizations require technology cybersecurity solutions and a solid process to detect and prevent threats and fix a breach of cybersecurity.
How does cybersecurity actually work? The Cybersecurity Essentials

What is cybersecurity from the point of view of your enterprise? A successful cybersecurity strategy must be based on several security tiers. Solutions from cybersecurity firms guarantee a strong defense against cyberattacks seamlessly.
People, infrastructure, vulnerabilities, and technology must all be considered in a comprehensive strategy for effective cybersecurity. Employees must understand data security standards. Organizations should establish a strong cybersecurity framework to protect critical systems, identify and combat risks, and recover quickly. By protecting devices, cloud systems, and networks, vulnerabilities—including those resulting from remote work arrangements—are crucial. At last, by utilizing advanced technologies like antiviruses, email protection tools, and new types of firewalls to ensure maximum level protection.
The Different Cybersecurity Types
1. Network Security
Network security solutions are being made to recognize and stop major cyberattacks. In order to enforce safe web use policies and conditions, these solutions include information and access controls.
Sandboxing, NGAV (Next-Gen Antivirus), IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), etc., are instances of advanced and multi-layered network threat prevention technologies. Automated SOAR technologies, threat hunting, and network analytics are also crucial.
2. Cloud Security: Best for organizational cybersecurity

Cloud security is becoming a top priority for businesses. Applications, data, infrastructure, and other components of an organization that are fully cloud-delayed are protected from attack for the grace of cybersecurity solutions and policies that are one of the key parts of a cloud security strategy.
Even though a lot of cloud providers provide security solutions, these are often insufficient to accomplish enterprise-grade or any higher-grade cloud security. Additional third-party solutions are required to protect data and attacks in the cloud.
3. Endpoint Security

The zero-trust security model recommends forming small units around data wherever it is in point. Endpoint security is one method to achieve protection with a workforce that roams. Endpoint security allows businesses to prevent end-user devices. By implementing data and network security controls, advanced cyber attack prevention like anti-phishing and anti-ransomware technologies such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
4. Mobile Security: Need Data Protection Strategies
Mobile devices, like tablets and smartphones, have access to corporate data and are subsequently vulnerable to threats from malicious apps and IM (instant messaging) attacks. Mobile security protects against rooting and jailbreaking attacks on operating systems and devices.
5. IoT Security and IT Security Measures
The deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices significantly boosts productivity; however, it concurrently exposes organizations to new cyber threats. Malicious entities actively seek out vulnerable devices that are inadvertently connected to the Internet, exploiting them for detrimental purposes, such as unauthorized access to corporate networks or incorporation into a global botnet.
To protect IoT devices, security strategies include the identification of all connected devices of the IoT and the use of Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). It’s a virtual security update to prevent potential exploits targeting weak devices of the IoT. Furthermore, the firmware of the device can be upgraded wirelessly to reduce vulnerabilities and defend against runtime attacks.
6. Application Security
Web applications, similar to other entities linked to the Internet, are vulnerable to threats from malicious actors. Since 2007, OWASP has monitored the ten most significant threats to essential web application security vulnerabilities, including issues like injection, broken authentication, misconfiguration, and cross-site scripting, among others.
By implementing application security measures, organizations can effectively mitigate the OWASP Top 10 attacks. Additionally, application security safeguards against bot attacks and curtails any harmful interactions with applications and APIs. Through ongoing education and adaptation, applications can maintain their security even as DevOps introduces new updates.
Gen V Attacks
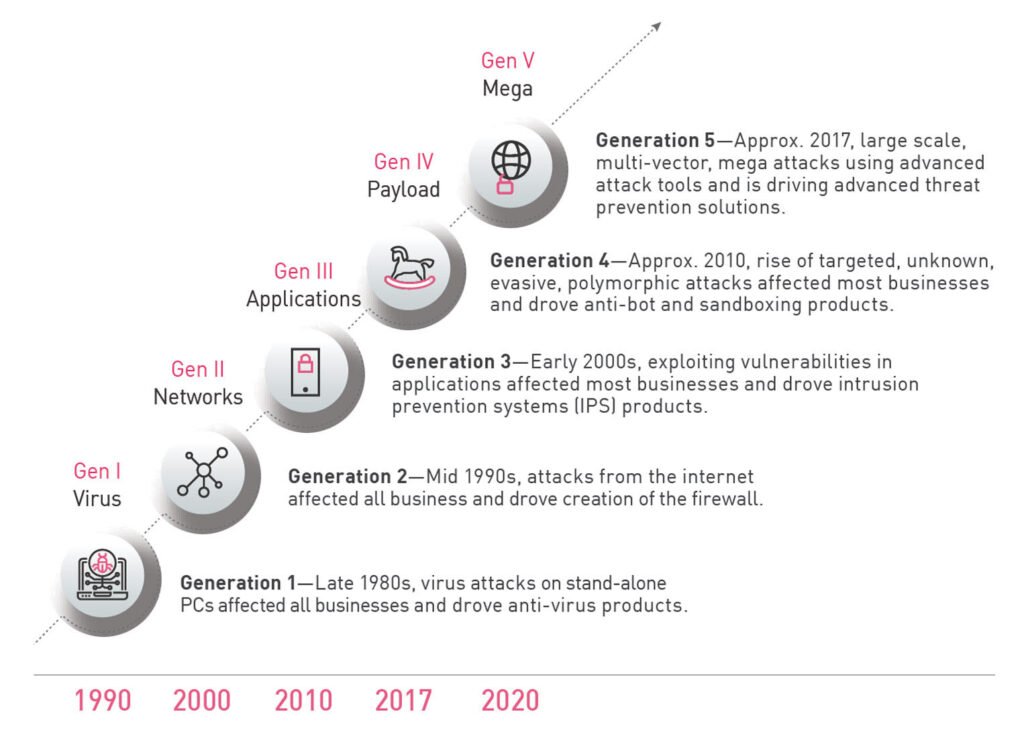
Generation V, or Gen V, cyberattacks differ from their predecessors in vast ways. The most notable distinction is the broad range of technologies that can be targeted, from mobile phones to entire cloud networks. Gen V attacks can spread across multiple countries, multiple businesses, and even multiple continents.
To learn more about the latest types of cybersecurity, cyber defense techniques, business cybersecurity, and IoT security, please visit the top sites like TechTarget, Checkpoint (best for Information Security Tips), and CheckFirewalls.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 6 types of cybersecurity?
This article discusses six types of cybersecurity measures: network security, application security, information security, cloud security, IoT security, and identity and access management. These measures can help protect organizations and individuals from cyber attacks.
What exactly does cybersecurity do?
Cybersecurity is the application of technologies to processes and controls to protect systems, networks, programs, devices, and data from cyberattacks.
Who needs cybersecurity?
Cybercrime is becoming increasingly serious. Strong cybersecurity is required to combat it. Cyberattacks and data breaches threaten individuals, governments, non-profit organizations, and educational institutions alike.


