Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a buzzword, often creating confusion for those unfamiliar with the technical aspects. But what is AI in simple words, and how does it work? This blog post will break down AI concepts, illustrate real-world examples, and show how AI is shaping the future. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of AI basics and applications, with practical examples that bring clarity to the topic.
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in Simple Words With Example
Artificial Intelligence, often shortened as AI, refers to the capability of machines to imitate human intelligence. In simple terms, AI allows computers to think and learn like humans, performing tasks that require problem-solving, decision-making, and sometimes even creativity.
AI’s significance in today’s world is enormous. From healthcare to transportation, AI is revolutionizing industries by increasing efficiency and improving decision-making. But with all the jargon surrounding it—machine learning, deep learning, neural networks—it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. This article aims to explain Artificial Intelligence in simple words with examples, giving you an easy-to-understand view of the world of AI.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the technology that makes it possible for computers and other devices to mimic human autonomy, creativity, problem-solving, learning, and comprehension.
AI-enabled apps and gadgets are able to see and recognize items. They are able to comprehend and react to human words. They are able to pick up new skills and knowledge. Both users and specialists can receive thorough recommendations from them. They are capable of acting on their own, negating the requirement for human knowledge or involvement (a self-driving automobile is a classic example).
However, in 2024, the majority of AI practitioners and researchers—as well as the majority of AI-related news—are concentrated on developments in generative AI (gen AI), a field of study that develops original text, graphics, videos, and other types of material. It’s critical to first comprehend machine learning (ML) and deep learning, the two technologies that underpin generative AI tools, in order to completely comprehend generative AI.
It is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes recognizing patterns, solving problems, making decisions, and even mimicking human conversations.
AI is not one single technology but an umbrella term encompassing various subfields such as machine learning and deep learning.
- Machine Learning Explained: Machine learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Think of it like teaching a computer by feeding it lots of examples, and it gradually learns to make predictions or decisions.
- Deep Learning Explained: Deep learning, on the other hand, is a type of machine learning modeled after the human brain’s neural networks. It excels at recognizing complex patterns, making it perfect for applications like image recognition or voice assistants.
The key principles of AI revolve around creating algorithms that can process information, learn from data, and improve over time. In essence, AI systems learn through experience, much like humans do.
What is intelligence?
Even the most complex insect activity is typically not interpreted as a sign of intelligence, whereas all human behavior but the most basic is. What makes the difference? Examine the actions of Sphex ichneumoneus, the digger wasp. When the female wasp comes back to her burrow with food, she puts it on the threshold, looks inside to see if there are any intruders, and only then, if all is well, brings her food inside.
The full nature of the wasp’s innate behavior is exposed if the food is moved a few inches away from the entrance to her burrow while she is inside: on emerging, she will repeat the whole operation as frequently as the food is displaced. Given the wasp’s glaring lack of intelligence, intelligence must entail the capacity to adjust to changing conditions.
Key Concepts of AI
To fully grasp AI, it’s essential to understand some key concepts that make up its foundation:
- Neural Networks Explained: Neural networks are the backbone of deep learning. They mimic the structure of the human brain, consisting of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process information. Neural networks allow machines to perform complex tasks, such as identifying faces in photos.
- Computer Vision Explained: Computer vision is the ability of AI systems to interpret and understand visual information from the world. It’s how self-driving cars “see” their surroundings or how your smartphone detects faces in photos.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Explained: NLP enables AI systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Examples include chatbots or virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, which can answer questions and perform tasks based on voice commands.
These concepts work together, allowing AI to process vast amounts of information and make intelligent decisions. For example, in autonomous vehicles, AI uses computer vision to “see” the road, neural networks to process that visual information, and NLP to communicate with passengers.
Real-World Applications of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries across the globe with its ability to automate processes, enhance decision-making, and improve efficiency. AI applications span a wide range of fields, from healthcare to finance, transportation, and entertainment. Here are some key areas where AI is making an impact:
1. Healthcare
AI is transforming healthcare by improving diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. Some key applications include:
- Medical Imaging: AI-powered tools assist doctors in detecting diseases like cancer by analyzing medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs).
- Personalized Medicine: AI helps create tailored treatment plans based on a patient’s genetics, lifestyle, and medical history.
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-driven chatbots provide 24/7 patient support, answering health-related questions and managing appointments.
- Robotic Surgery: AI-powered robots assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive surgeries with high precision.
2. Finance
In the financial industry, AI is widely used for:
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms analyze transaction patterns to detect and prevent fraudulent activities in real time.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI helps in making trading decisions by analyzing large volumes of market data, improving the speed and accuracy of financial transactions.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants streamline customer support by handling common queries and guiding users through financial processes.
- Risk Management: AI models predict financial risks and help organizations optimize their investment strategies.
3. Transportation
AI is revolutionizing the transportation sector, particularly in:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use AI for navigation, obstacle detection, and decision-making on the road.
- Traffic Management: AI systems analyze real-time traffic data to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: AI improves supply chain efficiency by predicting demand, optimizing routes, and managing inventory levels.
4. Retail and E-Commerce
AI plays a significant role in enhancing customer experiences in retail:
- Recommendation Engines: E-commerce platforms like Amazon use AI to suggest products based on user behavior and preferences.
- Inventory Management: AI helps retailers optimize stock levels and predict consumer demand to prevent shortages or overstock.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI chatbots provide instant customer support, guiding shoppers and addressing common inquiries.
5. Entertainment
AI is transforming the way we consume media and entertainment:
- Content Recommendation: Platforms like Netflix and YouTube use AI to recommend shows, movies, and videos based on viewing history.
- Content Creation: AI tools assist in generating music, art, and writing, enhancing creativity in fields like music composition and scriptwriting.
- Video Game Development: AI powers non-player characters (NPCs) and adaptive game environments, offering players more immersive experiences.
6. Education
AI is making learning more personalized and accessible:
- Smart Tutors: AI-based systems offer personalized learning paths and recommendations based on student performance.
- Automated Grading: AI tools can assess and grade exams and assignments, freeing up time for educators.
- Virtual Classrooms: AI-powered platforms enable interactive online learning experiences and real-time feedback.
7. Manufacturing
AI is enhancing productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing sector:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI systems analyze equipment data to predict when machinery might fail, helping avoid costly downtime.
- Robotics: AI-powered robots perform repetitive tasks, such as assembly and packaging, improving precision and speed.
- Quality Control: AI uses machine vision to detect defects in products during the manufacturing process.
8. Agriculture
AI applications in agriculture are helping optimize farming practices:
- Precision Agriculture: AI tools analyze soil data, weather conditions, and crop health to help farmers make informed decisions.
- Drones and Sensors: AI-powered drones monitor fields and detect crop diseases or water shortages in real time.
- Automated Harvesting: AI-driven robots assist in harvesting crops efficiently, improving yield and reducing labor costs.
9. Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service:
- 24/7 Availability: AI-driven support systems provide round-the-clock customer service, reducing response times and improving user experience.
- Personalized Interaction: AI tailors customer interactions based on preferences, purchase history, and behavior, enhancing satisfaction.
- Multi-Channel Support: AI integrates across multiple communication platforms (email, social media, live chat) to streamline customer service operations.
10. Cybersecurity
AI enhances cybersecurity by providing advanced threat detection and defense:
Behavioral Analysis: AI tracks user behavior to detect potential insider threats or malicious activities.
Threat Detection: AI analyzes network activity and identifies abnormal patterns that may indicate cyber threats or breaches.
Automated Response: AI systems can automatically respond to security incidents, containing threats before they spread.
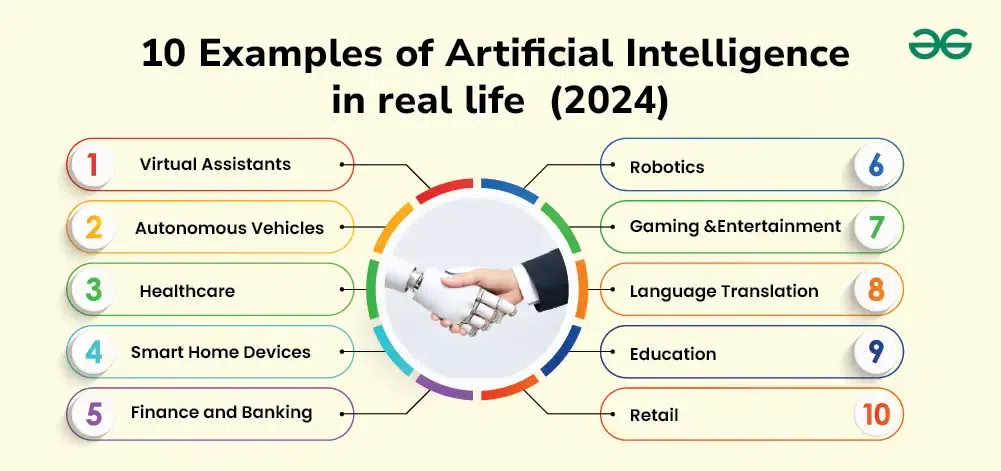
Everyday Examples of AI
Artificial intelligence is not just something confined to high-tech labs or industrial applications; it’s present in our daily lives. Here are some familiar examples of AI at work:
- Virtual Assistants: AI powers virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, helping users schedule tasks, answer queries, or control smart devices via voice commands.
- Recommendation Systems: Have you noticed how Netflix or YouTube always seems to suggest the perfect movie or video? That’s AI at work. These platforms use algorithms to analyze your behavior and make personalized recommendations.
- Smart Home Devices: Devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and home assistants use AI to automate household tasks, learn your preferences, and make life more convenient.
- Writing with AI: AI-powered tools that help normal users or professionals write content for their industry with a huge accuracy of grammar and fluency. (e.g. ChatGPT, and Google Gemini)
These examples highlight how AI is increasingly becoming part of everyday life, improving convenience and providing customized experiences.
The Role of Machine Learning in AI
Machine Learning (ML) plays a central role in AI’s functionality. It is the method through which AI systems can “learn” from data. Instead of being programmed with specific instructions, a machine learning system is fed vast amounts of data and taught to make predictions or decisions based on that information.
- Spam Filters: One practical example of machine learning is spam filters in your email. The system learns from previous emails marked as spam and continues improving its ability to detect unwanted emails.
- Search Filters: Automatic suggestions from Google or Bing as the intent of the users who are using the search engine. (e.g. Google Auto Suggestion or Microsoft Auto Suggestion)
- Image Recognition: Another common application is image recognition, where ML algorithms identify objects in images. This is how Facebook can tag friends in photos, or how self-driving cars recognize pedestrians or traffic signs.
By allowing AI systems to learn and improve from data, machine learning has unlocked a vast array of applications and continues to drive advancements in the field.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses complex structures called neural networks to process information in a way that mimics the human brain. These neural networks are made up of layers of nodes (also known as neurons), where each layer processes information and passes it to the next layer. This layered structure allows the network to learn and make decisions based on the data it processes.
Key Applications of Deep Learning:
- Facial Recognition:
- Deep learning is crucial in facial recognition technology. It helps systems not only recognize faces but also distinguish between different individuals with high accuracy. This is achieved by training the neural network on a large dataset of facial images, allowing it to learn the unique features of each face.
- Voice Assistants:
- Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa use neural networks to understand and respond to voice commands. These systems process natural language, which involves understanding the nuances of human speech. Over time, they continuously learn and improve their ability to understand and respond accurately.
Why Are These Advancements Important?
The advancements in deep learning and neural networks have significantly enhanced the capabilities of AI systems. Here’s why:
- Complex Problem Solving: Deep learning allows AI to handle tasks that were previously too complex for machines, such as understanding natural language, recognizing images, and making decisions based on large amounts of data.
- Continuous Improvement: Neural networks can learn from new data, which means they can continuously improve their performance over time.
- High Accuracy: The ability to process information through multiple layers allows these systems to achieve high accuracy in tasks like facial recognition and voice processing.
In summary, deep learning and neural networks are at the core of many advanced AI applications, making them more powerful and capable of performing complex tasks with high accuracy.
The Impact of AI on Society
AI is transforming society in both positive and challenging ways. On the positive side, AI is improving productivity, creating new job opportunities, and enhancing our daily lives through automation. However, there are concerns as well.
- Job Displacement: One of the main concerns is job displacement, particularly in industries like manufacturing and customer service, where automation may replace human workers.
- Privacy Issues: With AI systems collecting vast amounts of personal data, privacy concerns are growing. Questions about how data is used, stored, and protected are becoming increasingly important.
- Ethical Considerations: There are also ethical challenges regarding how AI should be developed and deployed, particularly in areas like facial recognition and surveillance.
The responsible use of AI is critical to ensuring that its benefits outweigh the potential risks.
The Future of AI
The future of AI is incredibly promising, with advancements on the horizon that could redefine industries and society as a whole. Some potential developments include:
- Healthcare Innovations: AI could play a central role in personalized medicine, using genetic data to create tailored treatment plans for individuals.
- Advanced Automation: In industries like manufacturing, AI-driven automation will likely lead to smarter factories and more efficient production processes.
- New Applications: Emerging fields like AI-powered cybersecurity, autonomous drones, and enhanced human-computer interaction could lead to groundbreaking innovations in the coming decades.
Staying informed about AI’s development is crucial, as these technologies will shape the future of work, communication, and everyday life.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant concept—it’s here, and it’s transforming the world around us. From machine learning and neural networks to real-world applications like healthcare and finance, AI is touching every aspect of our lives. By understanding Artificial Intelligence in Simple Words With Examples, you gain valuable insight into how this technology works and how it will continue to influence the future.
Whether it’s improving efficiency in the workplace or making our homes smarter, AI is reshaping society. As AI technology evolves, it’s essential to remain aware of its implications, both the opportunities it presents and the challenges it brings.