Introduction
Imagine waking up one morning to find your email hacked, your bank account compromised, or your personal photos leaked online. Scary, right? In today’s digital age, cybersecurity isn’t just for tech experts—it’s for everyone. Every click, download, or login is an opportunity for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities. So, how do you stay ahead of these cyber threats?
Welcome to your ultimate cybersecurity guide. Whether you’re a casual internet user, a small business owner, or a tech-savvy professional, this guide will arm you with practical tips and strategies to safeguard your online presence. From managing passwords to avoiding phishing scams, we’ll cover everything you need to know to stay secure in this ever-evolving digital landscape.
Let’s dive into the 5 ultimate strategies that can transform your cybersecurity habits—and ensure peace of mind every time you go online.
What is cybersecurity?

Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, devices, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. It involves implementing technologies, processes, and policies to safeguard digital information and infrastructure from cyber threats.
Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is crucial because it protects sensitive data, personal information, intellectual property, and critical infrastructure from cybercriminals. Without this ultimate cybersecurity guide, organizations and individuals are vulnerable to data breaches, financial loss, identity theft, and other malicious activities.
In today’s interconnected world, the risk of cyber attacks is ever-present, making cybersecurity essential for maintaining privacy, security, and trust.
Main Threats in Cybersecurity

There are several common cybersecurity threats that individuals and organizations face:
- Malware: Malicious software such as viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware that can damage or disrupt systems.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Deceptive tactics used to trick people into revealing confidential information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a system or network to make it unavailable to users.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and altering communication between two parties without their knowledge.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Long-term, targeted attacks aimed at stealing data or spying on organizations.
- Insider Threats: Employees or trusted individuals who misuse their access to harm the organization.
- Exploits and Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in software or hardware that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Why Learn Cybersecurity Basics and protect online privacy?
Learning the basics of cybersecurity is essential for several reasons:
- High Demand: Cybersecurity experts are in high demand across various industries, including government, banking, healthcare, and education.
- Job Opportunities: With cybersecurity skills, you can work in diverse fields and enjoy excellent salary benefits.
- Protecting Personal and Professional Data: Understanding cybersecurity basics helps you protect online privacy and that of your organization from cyber threats.
- Empowering Businesses: Cybersecurity knowledge enables companies to implement effective security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
- Staying Ahead of Threats: Cyber threat prevention are constantly evolving, and learning cybersecurity basics helps you stay informed and prepared to defend against new attacks.
You may read this Ultimate Cybersecurity Guide and the Hacker’s Roadmap.
Password Management Best Practices
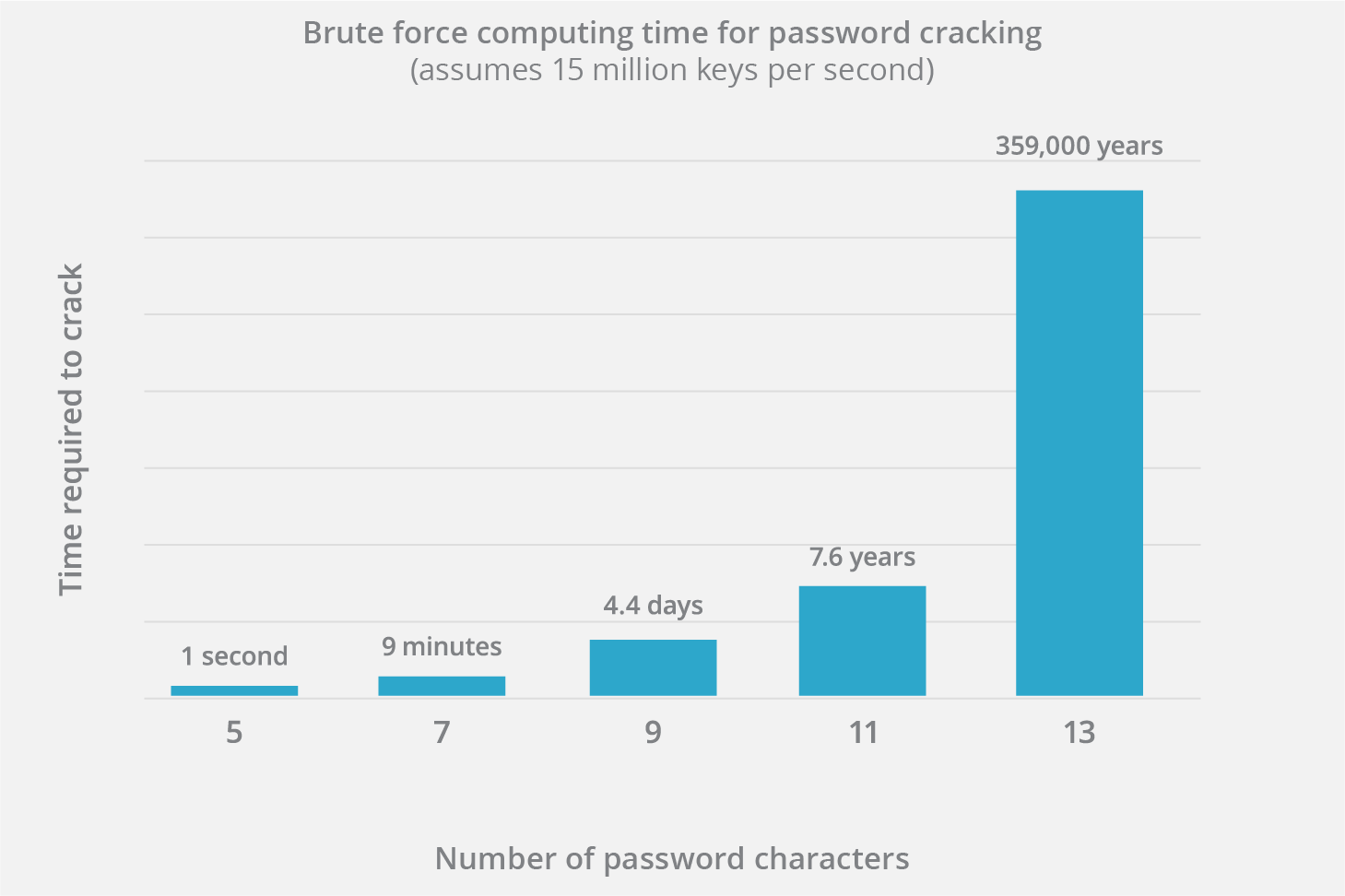
- Create Strong Passwords: Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Aim for at least 12 characters.
- Use Unique Passwords: Avoid reusing passwords across different accounts.
- Change Passwords Regularly: Update your passwords every few months.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security by enabling MFA2.
- Avoid Common Passwords: Don’t use easily guessable information like birthdays or common words.
- Use Password Managers: Tools like LastPass, Dashlane, or Bitwarden can help generate and store strong passwords.
Benefits of Hard Passwords
- Protect Personal Information: Strong passwords help safeguard your personal and financial information.
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: They make it difficult for hackers to gain access to your accounts.
- Enhance Security: Hard passwords reduce the risk of identity theft and data breaches.
Why Hard Passwords Are Not Easily Compromised
- Complexity: Hard passwords are difficult to guess or crack using brute-force attacks.
- Length: Longer passwords take more time and effort to crack.
- Randomness: Using a random mix of characters makes it harder for automated tools to guess.
RockYou2024: The Latest Password Compilation

RockYou2024 is the latest iteration of the infamous RockYou password list. Originally stemming from the 2009 RockYou hack, this list has grown significantly over the years. As of July 2024, the RockYou2024 database contains nearly 10 billion passwords.
This massive compilation includes passwords from both old and new data breaches, making it a valuable resource for penetration testers and cybersecurity researchers. However, it’s important to note that while the list is extensive, much of it consists of “junk” data that is of little use to hackers.
Nonetheless, it’s always a good idea to ensure you’re not reusing passwords across multiple services.
Have I Been Pwned: A Vital Security Tool

Have I Been Pwned is a free service created by security researcher Troy Hunt. It allows users to check if their email addresses or passwords have been compromised in a data breach.
By simply entering your email address, you can find out if it has appeared in any known breaches, helping you take proactive steps to secure your accounts. As of 2024, the service has grown to include over 71 million email addresses linked to hacked accounts.
Additionally, Have I Been Pwned offers notifications for future breaches, so you can stay informed and take action if your information is compromised.
Securing Your Devices to Keep Smartphones, Computers, and IoT Devices Safe with Cybersecurity Strategies
Benefits of Securing Devices
- Protects Personal Information: Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Prevents Financial Loss: Reduces the risk of financial theft and fraud.
- Maintains Privacy: Keeps personal communications and activities private.
- Ensures Device Longevity: Protects devices from malware and other threats that can degrade performance.
- Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements for data protection.
Why Mobile Phones Are Hacked
- Malware: Hackers install malicious software to steal data or control the device.
- Eavesdropping: To listen in on calls or read messages.
- Financial Gain: To steal money or payment information.
- Blackmail: To obtain sensitive information for extortion.
- Fun or Notoriety: Some hackers do it for the challenge or to show off their skills.
How Mobile Phones Are Hacked
- Phishing: Sending deceptive messages to trick users into revealing personal information.
- Malicious Apps: Installing apps that contain malware.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Taking advantage of software flaws in the operating system or apps.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi: Accessing devices through unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
- SS7 Vulnerability: Exploiting flaws in the cellular network to intercept calls and messages.
Why PCs Are Hacked
- Data Theft: To steal personal, financial, or business data.
- Financial Gain: To access bank accounts or make fraudulent transactions.
- Espionage: To gather sensitive information for competitive advantage.
- Disruption: To disrupt business operations or services.
- Ransomware: To encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release.
How PCs Are Hacked
- Phishing Emails: Sending emails that trick users into revealing login credentials.
- Malware: Installing malicious software to gain control of the system.
- Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities: Taking advantage of flaws in software programs.
- Brute Force Attacks: Trying multiple passwords until the correct one is found.
- Unsecured Networks: Accessing PCs through unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
How to Secure Devices
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Add an extra layer of security.
- Keep Software Updated: Install updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use Antivirus Software: Protect against malware and other threats.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Use secure, private networks whenever possible.
- Backup Data: Regularly back up important data to secure locations.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Only download apps and files from trusted sources.
Crucial Steps to Protect Devices
- Lock Devices: Use PINs, passwords, or biometric locks.
- Enable Auto-Lock: Set devices to lock automatically after a period of inactivity.
- Monitor App Permissions: Review and limit permissions for apps.
- Disable Unused Services: Turn off services and features you don’t use.
- Use Security Software: Install and update antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices.
The Ultimate Cybersecurity Guide
For a more detailed guide, you can refer to resources like Microsoft Support on Securing Your Device or the Ultimate Cybersecurity Guide by Norton.
Avoiding Phishing and Scams by knowing the Ultimate Cybersecurity Guide and Identifying and Protecting Against Common Online Scams
Phishing and scams are prevalent online threats that can lead to significant financial loss, identity theft, and compromised personal information. Here are some detailed steps to help you avoid these threats:
Educate Yourself on Phishing Tactics
Phishing involves tricking individuals into providing sensitive information by impersonating a trustworthy source. Common tactics include:
- Emails or Messages: Fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from legitimate sources, such as banks or government agencies.
- Spoofed Websites: Fake websites that mimic legitimate ones to steal login credentials.
- Phone Calls (Vishing): Scammers pretending to be from reputable organizations to extract personal information over the phone.
Think Before You Click
- Verify Senders and Links: Hover over links to check the URL before clicking. Look for subtle differences in domain names.
- Avoid Suspicious Attachments: Do not open unexpected attachments, as they may contain malware.
- Be Wary of Urgent Requests: Scammers often create a sense of urgency to pressure you into acting quickly without thinking.
Use Strong, Unique Passwords

- Create Complex Passwords: Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid Common Passwords: Do not use easily guessable passwords like “password123” or “qwerty.”
- Use Password Managers: Tools like LastPass or Bitwarden can generate and store strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Add an Extra Layer of Security: 2FA requires a second verification step, such as a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Use Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Authy provide time-based codes for added security.
Regularly Update Software and Security Patches
- Keep Systems Updated: Install updates for your operating system, browser, and other software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Set your devices to update automatically to ensure you’re always protected against the latest threats.
Recognizing Phishing Emails
- Unfamiliar Greetings: Phishing emails often start with generic greetings like “Dear Customer.”
- Spelling and Grammar Errors: Look for mistakes that legitimate organizations would not make.
- Suspicious Links: Hover over links to see if they lead to legitimate websites.
- Requests for Personal Information: Legitimate companies rarely ask for sensitive information via email.
Identifying Spoofed Websites
- Check the URL: Ensure the website address starts with “https://” and look for a padlock icon in the browser bar.
- Look for Red Flags: Poor design, spelling errors, and unusual domain names can indicate a spoofed site.
Avoiding Smishing Attacks with this ultimate cybersecurity guide
- Be Cautious with Text Messages: Do not click on links or provide information in response to unsolicited text messages.
- Verify Sender Identity: Contact the organization directly using a known phone number to confirm the legitimacy of the message.
Protecting Yourself from Vishing
- Do Not Share Personal Information: Hang up and call back using a verified number if you receive a suspicious call.
- Verify Caller Identity: Ask for the caller’s name, department, and phone number, then verify this information independently.
Beware of Urgent Requests
- Pause and Think: Scammers often create a sense of urgency to pressure you into acting without thinking.
- Verify Requests: Contact the organization directly to confirm the legitimacy of any urgent requests.
Question Unexpected Offers
- Be Skeptical: If an offer seems too good to be true, it probably is.
- Research: Look up the offer online to see if others have reported it as a scam.
Avoid Sharing Personal Information Online
- Limit Information Sharing: Be cautious about what personal information you share on social media and other online platforms.
- Use Privacy Settings: Adjust privacy settings to control who can see your information.
Use Secure Wi-Fi Networks
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Use secure, private networks whenever possible.
- Use VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) can encrypt your internet connection and protect your data.
Be Cautious on Social Media
- Limit Personal Information: Avoid sharing sensitive information on social media.
- Adjust Privacy Settings: Use privacy settings to control who can see your posts and personal information.
Using Advanced Tools with this Ultimate Cybersecurity Guide to Employing VPNs, Antivirus Software, and Firewalls for Additional Hacking Protection
- VPNs: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) encrypt your internet traffic, providing privacy and security, especially on public Wi-Fi. Popular VPNs in 2024 include Norton, TotalAV, and Avast, which offer robust encryption and additional features like ad blockers and no-log policies.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software detects and removes malware, viruses, and other threats. Leading antivirus solutions in 2024 include Norton, Bitdefender, and McAfee, which offer comprehensive protection and additional features like VPNs and anti-phishing tools.
- Firewalls: Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. They are essential for protecting your network from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are transforming various industries by automating tasks, providing predictive analytics, and enhancing decision-making processes. Key frameworks include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn, which are widely used for developing AI models.
Harnessing the Power of Automation
- Automation: Automation tools streamline repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce human error. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a popular method for automating routine business processes, while advanced automation solutions integrate AI to handle more complex tasks.
Exploring Data-Driven Insights
- Data-Driven Insights: Data analytics tools help businesses make informed decisions by analyzing large datasets. Predictive analytics, machine learning models, and data visualization tools are essential for extracting valuable insights from data.
Optimizing Processes with Advanced Technologies
- Advanced Technologies: Technologies like AI, machine learning, and automation are used to optimize business processes, improve productivity, and reduce costs. These technologies enable businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and stay competitive.
Embracing Digital Transformation
- Digital Transformation: Digital transformation involves integrating digital technologies into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value to customers. This includes adopting cloud computing, AI, big data analytics, and other advanced technologies.
Implementing AI-Powered Solutions
- AI-Powered Solutions: AI-powered solutions are used to enhance various business functions, including customer service, marketing, and operations. Examples include chatbots, predictive analytics, and personalized recommendations.
Utilizing Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models analyze historical data to predict future trends and outcomes. This is widely used in industries like finance, healthcare, and marketing to forecast market trends, customer behavior, and potential risks.
Applying Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- NLP: Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and process human language. Applications include chatbots, sentiment analysis, and language translation. Leading frameworks for NLP include TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Leveraging Computer Vision for Image and Video Analysis
- Computer Vision: Computer vision technologies analyze images and videos to extract meaningful information. Applications include facial recognition, object detection, and video surveillance. Popular tools include OpenCV and TensorFlow.
Automating Repetitive Tasks with RPA
- RPA: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive and rule-based tasks, improving efficiency and accuracy. RPA tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere are widely used in various industries.
Streamlining Workflows with Automation Tools
- Automation Tools: Automation tools help streamline workflows by automating routine tasks and processes. This includes workflow automation software, project management tools, and integration platforms.
Building Intelligent Automation Solutions
- Intelligent Automation: Intelligent automation combines AI and RPA to create more advanced automation solutions. These solutions can handle complex tasks, make decisions, and learn from data.
Integrating Automation into Business Processes
- Integration: Integrating automation into business processes involves identifying repetitive tasks, implementing automation tools, and continuously optimizing workflows. This helps businesses achieve greater efficiency and scalability.
Regular Updates and Backups: Importance of Keeping Software Updated and Maintaining Data Backups
Software Updates
- Importance: Keeping software up-to-date is crucial for security and performance. Updates often include patches for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
- Automatic Updates: Set up automatic updates to ensure your software is always patched without manual intervention.
- Secure Connections: Ensure your device is connected to a secure network before installing updates.
Backups
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your data to protect against loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or human error.
- Backup Methods: Use a variety of methods such as cloud storage, external hard drives, and network-attached storage (NAS).
- Testing Backups: Test your backups regularly to ensure they are working properly and can be restored when needed.
Digital Hygiene Tips: Managing Online Presence and Digital Footprint Responsibly
Passwords
- Strong, Unique Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords.
- Password Managers: Use a password manager to help you keep track of your passwords and generate strong ones.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Enable 2FA: Enable 2FA on all accounts that support it. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of identification, such as a code sent to your phone.
Managing Online Presence
- Privacy Settings: Regularly review and adjust privacy settings on social media and other online platforms to control who can see your information.
- Be Cautious with Personal Information: Be mindful of the personal information you share online and avoid sharing sensitive details.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your online security settings and adjust them as needed.
Top Data Security Tips to Protect Your Information
In an era where data breaches and cyberattacks are increasingly common, safeguarding your personal and professional data has never been more critical. Whether you’re an individual user or a business owner, following these data security tips will help you protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
1. Use Strong and Unique Passwords
- Create passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts.
- Use a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords securely.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Add an extra layer of security by enabling MFA on your accounts.
- Use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy instead of relying on SMS-based codes.
3. Keep Software Updated
- Regularly update your operating system, applications, and antivirus software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enable automatic updates where possible to ensure you don’t miss critical security patches.
4. Be Cautious with Emails and Links
- Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown senders.
- Verify URLs by hovering over links to ensure they lead to legitimate websites.
- Look out for red flags in emails, such as poor grammar or unusual requests for sensitive information.
5. Encrypt Sensitive Data
- Use encryption tools to protect files containing sensitive information.
- Always encrypt emails when sending confidential documents.
6. Backup Data Regularly
- Schedule regular backups of important files and store them securely, such as in encrypted cloud storage or external drives.
- Test your backups to ensure data can be restored when needed.
7. Use Secure Wi-Fi Networks
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi for accessing sensitive accounts or sharing confidential information.
- Use a VPN to encrypt your internet connection when using public or untrusted networks.
8. Limit Personal Data Sharing
- Be cautious about sharing personal information on social media or public forums.
- Adjust privacy settings on social platforms to control who can view your information.
9. Monitor Account Activity
- Regularly review your bank statements, credit card activity, and online accounts for suspicious behavior.
- Use tools like Have I Been Pwned to check if your email or passwords have been compromised in data breaches.
10. Implement Strong Security Policies (For Businesses)
- Educate employees on best practices for data security and phishing prevention.
- Restrict access to sensitive data to only those who need it.
- Use endpoint protection solutions to safeguard devices within the organization.
11. Secure Physical Devices
- Use device locks (PIN, fingerprint, or facial recognition) for your phone, laptop, and tablets.
- Avoid leaving devices unattended in public places.
- Encrypt storage drives to protect data in case of theft.
12. Disable Unnecessary Permissions and Services
- Review app permissions on your devices and disable those that are unnecessary.
- Turn off services like Bluetooth or location sharing when not in use.
13. Beware of Social Engineering Attacks
- Don’t disclose sensitive information to unknown individuals, even if they claim to be from a trusted organization.
- Verify requests through official channels before taking any action.
14. Use Advanced Security Tools
- Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices.
- Set up firewalls to monitor and block unauthorized access to your network.
- Consider tools with AI-based threat detection for advanced protection.
Know more about Online safety strategies here
Conclusion: The Digital Life Security
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is more important than ever. By following these five essential practices, you can significantly enhance your online security and protect your personal information:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Passwords are your first line of defense. Ensure they are complex and unique for each account.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your software to patch vulnerabilities and keep your systems secure.
- Email Awareness: Be vigilant about phishing attempts and verify the sender’s identity before clicking on links or opening attachments.
- Secure Networks: Use VPNs to encrypt your internet connection, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Privacy Settings: Manage your online presence by adjusting privacy settings and being cautious about the information you share.
FAQs and Answers
Why is it important to use strong, unique passwords?
Strong, unique passwords are harder for attackers to guess or crack, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts.
What are some common signs of a phishing email?
Look for spelling and grammar errors, unexpected requests for personal information, and suspicious links or attachments.
How does a VPN protect my data?
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
What should I do if I receive an unexpected email asking for personal information?
Do not respond or click on any links. Verify the sender’s identity by contacting the organization directly using a known phone number or email address.


