Your digital footprint—the trail of data left behind every time you interact online—can reveal more about you than you might expect. From social media posts to online transactions, your digital presence can be exploited by cybercriminals if left unprotected. This guide explores advanced techniques to secure your digital footprint and safeguard your online privacy.
The Importance of Securing Your Digital Footprint
What is a Digital Footprint?
A digital footprint comprises all the data and information you leave online—whether actively (like social media posts or emails) or passively (like location data or browsing habits). Everything from cookies to account logins contributes to this trail, making it a goldmine for hackers and trackers.
Why is securing your digital footprint crucial?
Failing to secure your digital footprint can lead to significant risks, including:
- Identity theft: Fraudsters can steal your personal data to impersonate you.
- Financial loss: Compromised accounts could drain your bank balance.
- Reputational damage: Past online posts or leaked information could harm your personal or professional life.
Proactively securing your digital footprint not only prevents such risks but also gives you greater control over your online privacy.
5 Advanced Tips to Secure Your Digital Footprint
Create Uncrackable Passwords
Passwords remain a cornerstone of online security. However, weak or reused passwords can be cracked easily through brute force attacks or credential stuffing. Here’s how to ensure your passwords are virtually unbreakable:
- Use password managers like LastPass or Dashlane to generate and store complex passwords.
- Opt for passphrases—a combination of unrelated words such as “Taco!Galaxy?Parrot7.”
- Never reuse passwords across platforms to reduce the risk of multiple account breaches.
A strong, unique password for every account ensures hackers face insurmountable barriers at the first point of entry.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to Secure Your Digital Footprint
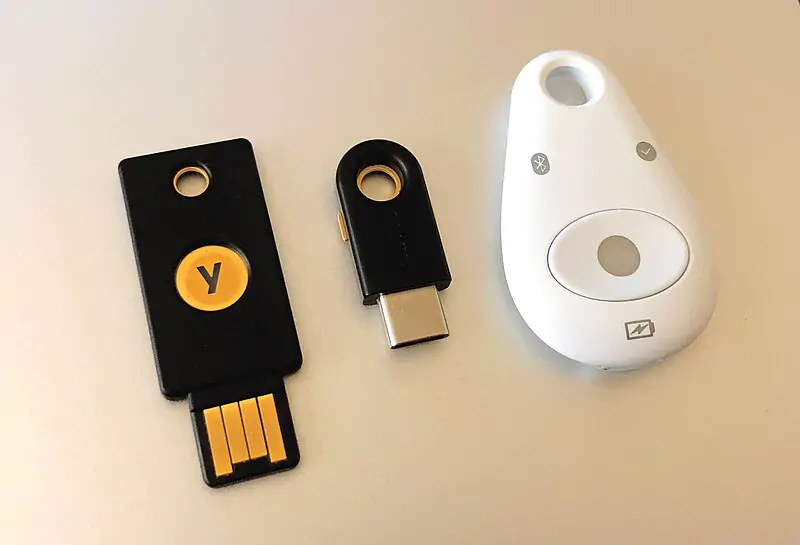

Even strong passwords can fail if stolen, but MFA adds an extra layer of security:
- Use biometric authentication (fingerprints or facial recognition) for sensitive accounts.
- Opt for app-based authenticators like Google Authenticator or Authy over SMS-based codes, which are vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
- Enable MFA wherever possible—bank accounts, email services, and social media platforms.
MFA ensures that even if someone gains access to your password, they won’t get through without the secondary authentication factor.
Regularly Update and Patch Devices
Outdated software is one of the most exploited vulnerabilities in cyberattacks that can unsecure your digital footprint. Hackers target unpatched systems to infiltrate devices and steal data. To stay secure:
- Enable automatic updates for operating systems, browsers, and apps.
- Regularly check for firmware updates for IoT devices, like smart home systems.
- Install patches immediately after release to minimize exposure to known vulnerabilities.
Keeping your software up-to-date ensures you’re always protected against the latest threats.
Review Permissions
Excessive permissions granted to apps and websites expose your data unnecessarily. To reduce risk:
- Regularly audit app permissions on your devices (e.g., location, camera, or microphone access).
- Limit permissions to only those absolutely required for functionality. For instance, a flashlight app doesn’t need access to your contacts.
- Review and delete unused accounts or apps to minimize data collection points.
Restricting permissions reduces the amount of personal data you share online, limiting the potential damage of data leaks.
Use Encrypted Communication Tools
Unsecured communication channels can expose sensitive information. Upgrade to encrypted platforms for better privacy:
- Use secure messaging apps like Signal or WhatsApp, which offer end-to-end encryption.
- Opt for email services such as ProtonMail, known for robust encryption.
- For sensitive file sharing, tools like Tresorit or SpiderOak provide secure options.
Encrypted communication ensures that even if intercepted, your data remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Common Threats to Digital Privacy
Understanding prevalent risks helps in crafting a robust defense. Here are some common threats to digital privacy:
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or messages to steal sensitive information.
- Data Breaches: Even trusted platforms can suffer breaches, exposing your data.
- Tracking Technologies: Cookies, trackers, and browser fingerprinting monitor your online activity for profiling or exploitation.
Awareness of these threats allows you to anticipate and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Best Tools for Digital Security

Arm yourself with trusted digital security tools:
- Password Managers: LastPass, Bitwarden
- VPNs: NordVPN, ExpressVPN for encrypted internet traffic
- Antivirus Software: Norton, Kaspersky for malware protection
- Secure Browsers: Brave, Firefox with privacy-focused extensions like uBlock Origin
These tools act as a fortress, ensuring that your digital footprint remains secure.
Future Trends in Digital Privacy
The landscape of digital privacy is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-Driven Privacy Tools: AI technologies are being deployed to detect and mitigate threats in real time.
- Decentralized Identity Solutions: Platforms like Microsoft’s Decentralized Identity Network aim to give users control over their data.
- Zero-Trust Security Models: Organizations are adopting stricter policies, assuming every interaction could be a potential threat.
Staying informed about these advancements helps you prepare for the future of online security.
Conclusion
Securing your digital footprint is more than a one-time task; it requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation. By following these advanced tips—using strong passwords, enabling MFA, keeping your software updated, limiting permissions, and leveraging encrypted tools—you significantly reduce your online risks. Take proactive steps today to ensure your online presence remains under your control, not someone else’s.


